Recession and stagflation are two of the most feared terms in economics. Both refer to periods of economic distress, but they occur under very different conditions and have different implications for policy makers, businesses, and individuals.
In this post, we’ll explore what they mean, how they differ, and why understanding the difference matters.
📉 What is a Recession?
A recession is a period of declining economic activity, typically recognized after two consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth.
🔑 Key Features of Recession:
- GDP falls
- Unemployment rises
- Consumer spending declines
- Business profits shrink
- Inflation usually remains low or stable
🧠 Example: The 2008 global financial crisis led to a major recession affecting most countries.
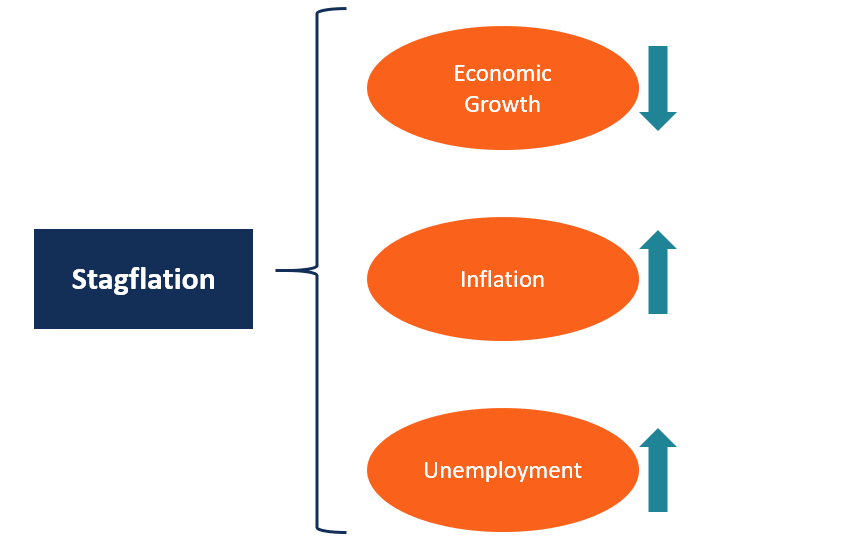
📊 What is Stagflation?
Stagflation is a rare economic condition where stagnant growth, high unemployment, and high inflation occur simultaneously.
🔑 Key Features of Stagflation:
- Little or no economic growth
- High inflation (prices rise)
- High unemployment
- Falling productivity
🧠 Example: The 1970s oil crisis led to stagflation in the U.S., with soaring prices and joblessness.
🔍 Recession vs Stagflation: Comparison Table
| Feature | Recession | Stagflation |
|---|---|---|
| Growth | Negative or very low | Stagnant or very low |
| Inflation | Low or deflationary | High |
| Unemployment | High | High |
| Cause | Demand-side shocks (e.g., less spending) | Supply-side shocks (e.g., oil prices, policy) |
| Monetary Policy | Can reduce interest rates to recover | Difficult – lowering rates worsens inflation |
| Example | 2008 Global Financial Crisis | 1970s Oil Crisis |
🧭 Policy Challenges
- ✅ In a Recession, central banks can usually stimulate the economy by cutting interest rates and increasing spending.
- ⚠️ In Stagflation, policies are tricky: lowering interest rates may fuel inflation, while raising them could worsen unemployment.
🤔 Why It Matters
Understanding the difference between recession and stagflation helps:
- Investors make better financial decisions
- Policymakers choose the right economic tools
- Citizens understand what’s affecting jobs, prices, and wages
📌 Conclusion
While both recession and stagflation indicate economic troubles, they come from different sources and require very different responses. Recession is about falling demand; stagflation is a dangerous mix of inflation and stagnation.