A lathe is a machine tool which is used to rotate a workpiece to perform various operations such as turning, facing, knurling, grooving etc., with the help of tools that are applied to the workpiece.
Working Principle of Lathe Machine
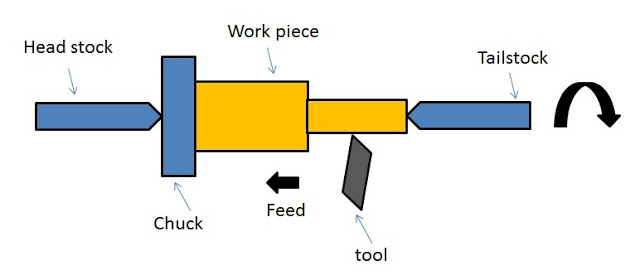
The function of a lathe is to remove metal from a piece of work to give it a desired shape and size. In a lathe machine, the workpiece rotates against the tool. The tool is used to remove material from the workpiece. The direction of the motion of the tool is called a feed.
Main Parts of Lathe Machine
The various main parts of lathe machine are
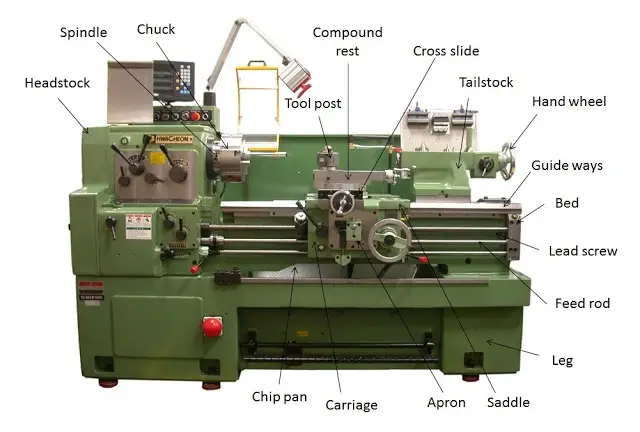
1. Headstock
It is present on the left-hand side of the lathe. It holds the gear train, main spindle, chuck, gear speed control levers, and feed controllers. It is aligned with the tailstock. The headstock is made up of cast iron.
(i) Chuck
It is that part of the lathe machine which is used to hold the workpiece. It is attached to the main spindle of the headstock. It rotates with the spindle and also rotates the workpiece. In the lathe machine, we generally use three-jaw or four-jaw check. The three jaw of the three jaw chuck is made to move simultaneously but the jaws of the four jaw chuck moves independently.
(ii) Main Spindle
This part of the lathe machine is used to hold cylindrical work piece within it. It is a hollow shaft on which the chuck is mounted.
(iii) Feed Selector
It is used to select the direction of the feed i.e. whether we want to move the tool from left to right or right to left. Feed selector is present on the headstock.
2. Tailstock
It is present at the right-hand side of the lathe. It is used to provide supports to the workpiece. It supports the workpiece from one end i.e. right end.
3. Bed
It is the main part of the lathe. All the parts of the lathe are bolted on the bed. It comprises of headstock, tailstock, carriage guideways and other parts. It is made of cast iron.
Guideways
Guideways are present on the bed. As its name indicates it is used to guide the tailstock and carriage. The tailstock and carriage slide over the guideways. It is an inverted V.
4. Carriage
The carriage is present in between the headstock and tailstock. It carries apron, saddle, compound rest, cross slide and tool post.
(i) Tool Post: It is used to hold the tool. It has T-slot for holding the tool. The tool post is bolted on the carriage.
(ii) Compound Rest: It is used to set the tool at a desired angle for taper turning and other operations.
(iii) Cross Slide: The cross slide is used to move the tool perpendicular to the axis of the lathe.
(iv) Saddle: The top portion of the carriage is called the saddle. Cross slide is mounted on the saddle.
(v) Apron: The front portion of the carriage is called apron. It contains all the moving and control mechanism of the carriage.
5. Lead Screw
The lead screw is used to move the carriage automatically during threading.
6. Feed Rod
It is used to move the carriage from left to right and vice versa.
7. Chip Pan
Chip pan is used to collect the chips that are produced during the lathe operation. It is present at the bottom of the lathe.
8. Hand Wheel
It is the wheel that is operated by hand to move the cross slide, carriage, tailstock and other parts that have handwheel.
Types of Lathe Machine
The lathe machine is generally divided into three types.
1. Engine lathe
2. Turret lathe
3. Special purpose lathe
Lathe Machine Operations
The various operations that we perform on the lathe are:
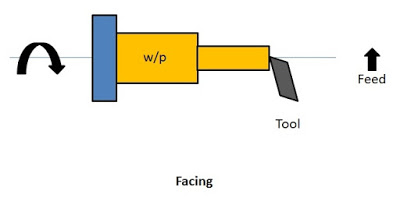
1. Facing
It is the first operation that is done on the workpiece. It is a machining operation that is done to produce flat surfaces at the ends of the workpiece. This operation is performed by feeding the tool perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the chuck.
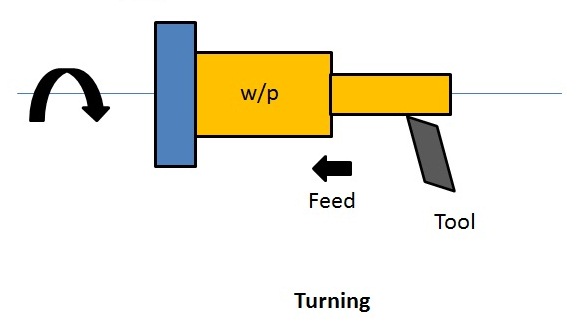
2. Turning
In turning operation, the excess material is removed from the surface of the workpiece to produce a cylindrical surface of desired shape and size. During the turning operation, the feed is moved along the axis of rotation of the chuck. It reduces the diameter of the cylindrical workpiece.
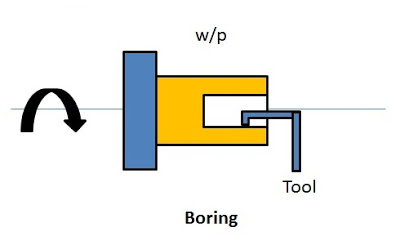
3. Boring
The process of removing material from hole of the workpiece is called boring. Holes are bored with the help of single point cutting tool.
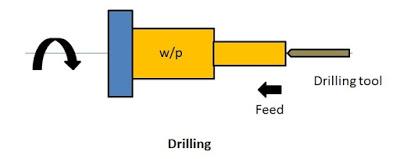
4. Drilling
It is the process of making holes in the workpiece by the use of drills. The drill is held in the tailstock and the drilling operation is done by advancing the drill in the workpiece by rotating the handle of the tailstock.
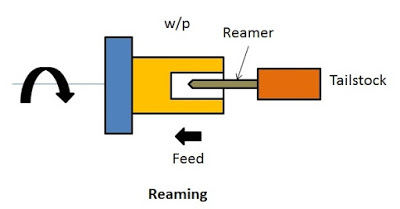
5. Reaming
The process of enlarging the holes to accurate sizes is called reaming. Reaming is always performed after drilling operation. It is similar to the drilling process. The reamer is held in the tailstock to carry out reaming operation.
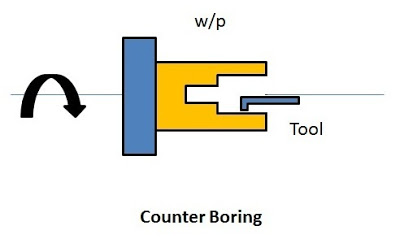
6. Counter Boring
The process of boring a hole to more than one diameter on the same axis is called counterboring. This operation is performed by boring tool.
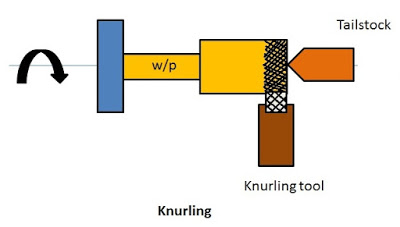
7. Knurling
It is the process of making indentations (recess or sharp depression) on the border of a workpiece. The knurling operation is done to provide a better grip to the job. It is performed by the knurling tool. The knurling tool is pressed against the job to perform the knurling operation.
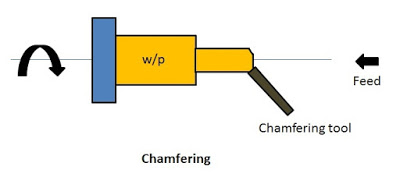
8. Chamfering
Chamfering is the process of beveling the extreme ends of a workpiece. It is done in order to remove the burrs, to protect the end of the workpiece from being damaged and to have a better look.
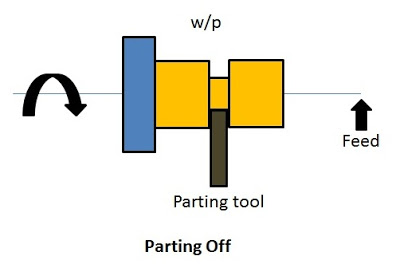
9. Parting Off
It is the process of cutting a workpiece after it has been machined to the required shape and size.
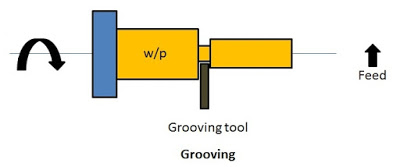
10. Grooving
The process of creating a narrow slot on the workpiece is called grooving. It is also known as recessing or necking
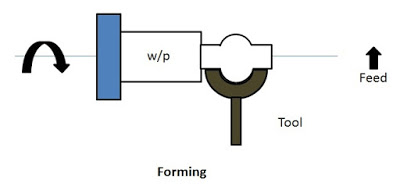
11. Forming
It is process in which a convex, concave or any irregular surface is formed on the workpiece with the help of a forming tool. Forming tool having the required shape is used to perform forming operation.
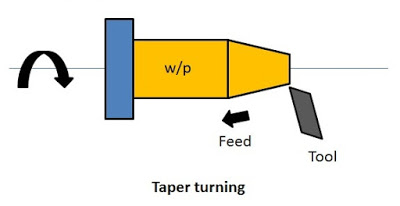
12. Taper Turning
It is the process in which a conical shape is produced on the workpiece. During taper turning the feed is set at an angle to the workpiece.
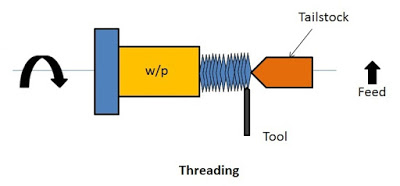
13. Threading
The process of making threads on a cylindrical job is called threading
14. Undercutting
In the undercutting operation, we enlarge the diameter if done internally and decrease the diameter if done externally. It is done at the end of the hole, near the stepped shoulder of a cylindrical surface and at the end of a threaded portion in the blot.
14. Eccentric Turning
It is a turning operation in which turning is performed at a different axis on a single setting of a job. This method of turning is generally used to produce crankshafts and camshafts.
Application of Lathe Machine
- The lathe machine is used in metal working, wood turning, metal spinning, parts reclamation, thermal spraying, and glass working.
- It can be used to shape pottery, the potter’s wheel is the latest well-known design made by a lathe.
- If we have most suitably equipped metal lathe then it can be used to produce most solids of revolution, plane surfaces, and screw threads or helices.
- Ornamental lathes can produce three-dimensional solids of incredible complexity.
- Examples of various objects that are produced by lathe are candlestick holders, gun barrels, cue sticks, table legs, bowls, baseball bats, musical instruments, crankshafts, and camshafts.


