✅ What is a Recession?
A recession is a significant decline in economic activity across the economy, lasting for months or even years. It is generally marked by:
- Falling GDP
- Rising unemployment
- Reduced consumer spending
- Lower industrial production and retail sales
📌 Technically, a recession is often defined as two consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth.
🔁 Why Does a Recession Happen?
| Cause | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 🔺 High inflation | Prices rise → people buy less → production slows down |
| 🏦 High interest rates | Loans become costly → spending and investment drop |
| 📉 Stock market crash | Wealth shrinks → consumer confidence falls |
| 🌍 Global shocks | Wars, pandemics, or oil crises impact global trade |
| 🏭 Low demand | Businesses earn less → layoffs → economic slowdown |
🎯 Impact of Recession on the Economy:
- Job losses and layoffs
- Lower income and profits
- Business closures
- Reduced tax collection
- Fall in stock market values
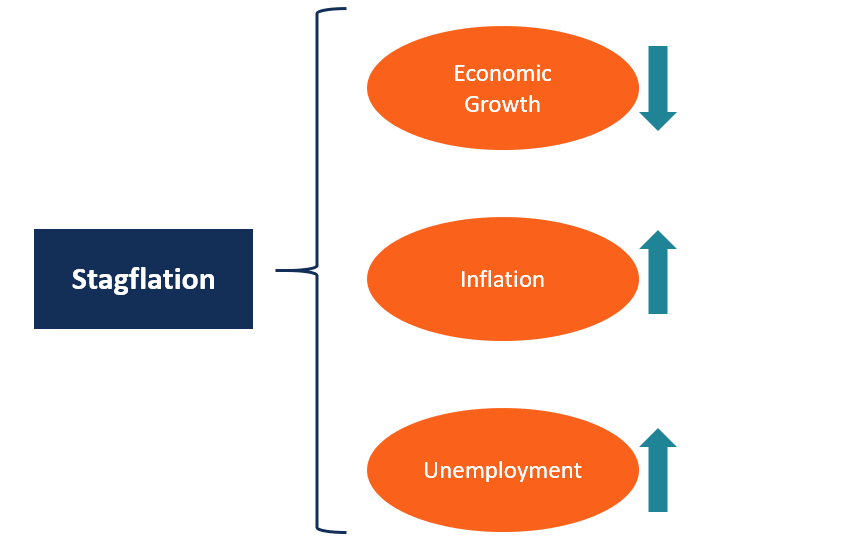
🧠 Difference Between Recession and Stagflation:
| Factor | Recession | Stagflation |
|---|---|---|
| Growth | Negative or very low | Low or stagnant |
| Inflation | Usually low | High |
| Unemployment | High | High |
| Cause | Demand-side (low spending) | Supply-side + demand mismatch |
Read more : Recession vs Stagflation