✅ What is Economic Growth?
Economic growth is the increase in the value of goods and services produced by an economy over time. It’s generally measured as the percentage increase in Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- GDP (Gross Domestic Product): The total monetary value of all finished goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific time period.
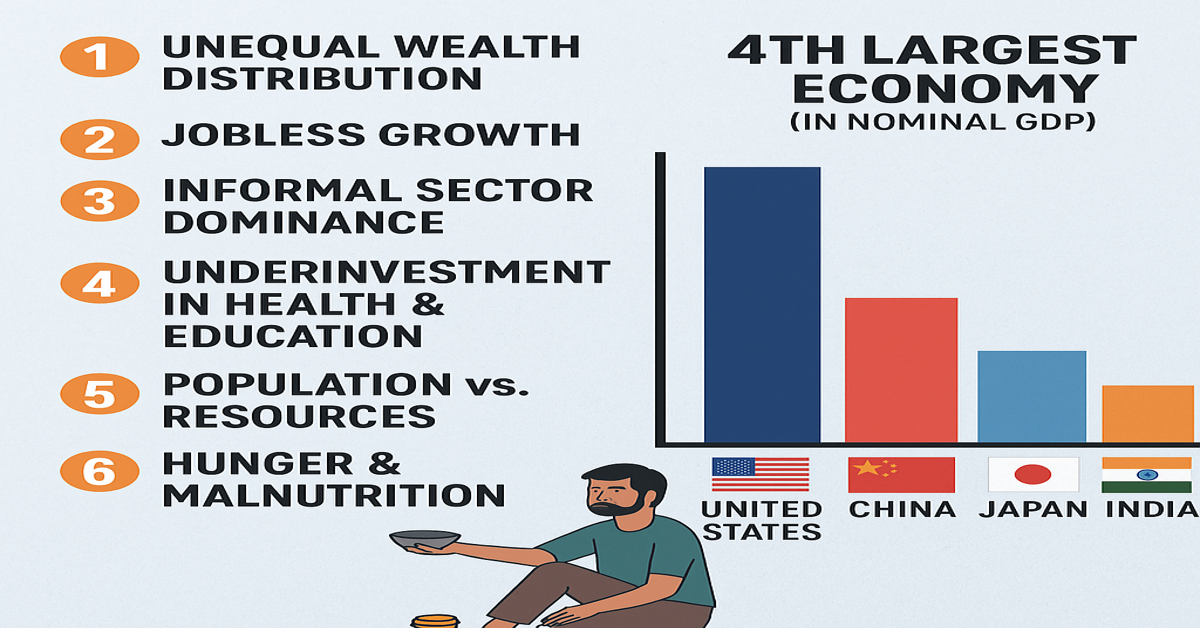
📌 So, economic growth is about the entire country’s economy (State or Nation).
✅ Is Economic Growth for the State or Individual?
Economic growth is:
- Primarily measured at the national (State) level.
- However, individuals benefit from economic growth when it leads to:
- More jobs
- Higher income
- Better public services
- Improved living standards
But the core definition of economic growth refers to the State-level or national economy, not individual wealth.
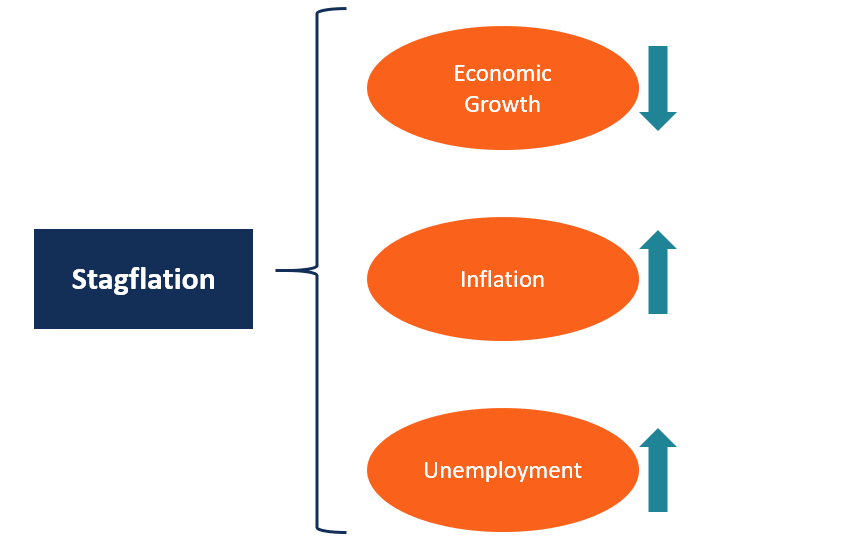
✅ Why is Economic Growth Slow During Stagflation?
Stagflation = Stagnation (low/no growth) + Inflation (high prices)
Here’s why growth slows down during stagflation:
| Reason | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 🔺 High Inflation | Prices of goods/services rise, reducing purchasing power. Consumers buy less. |
| 🔻 Low Demand | As things become expensive, people reduce spending → less demand for products. |
| ⚠️ High Unemployment | Businesses face high costs, profits drop, leading them to cut jobs. |
| 🛑 Reduced Investment | Inflation creates uncertainty; investors avoid risk, so businesses don’t expand. |
| 🏭 Production Falls | With low demand and high costs, factories produce less, reducing overall output. |
➡️ So during stagflation, both consumption and production suffer, which slows down economic growth.
🔁 Summary:
- Economic Growth = Increase in total goods/services produced (measured by GDP).
- It is for the State/Nation, not individuals, though individuals benefit indirectly.
- During Stagflation, growth slows because:
- High prices reduce demand
- Investment falls
- Jobs are lost
- Production declines
Let me know if you’d like a chart or infographic on this!