📌 Introduction
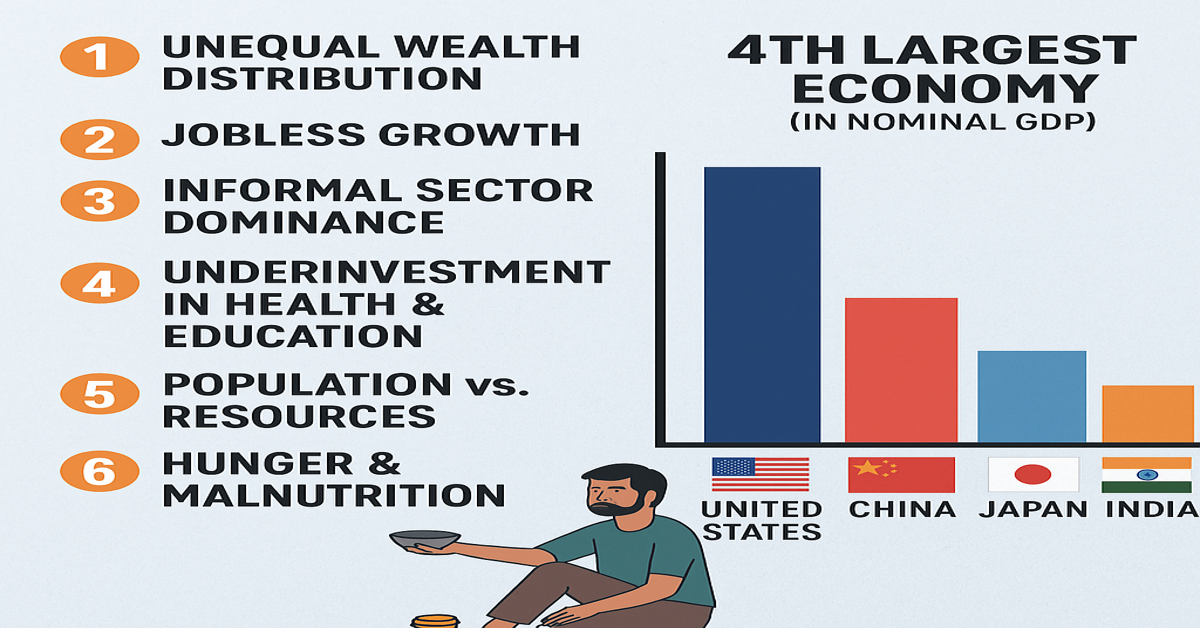
India recently became the 4th largest economy in the world by nominal GDP. Yet, deep social issues like poverty, unemployment, and hunger persist. Why? This article explores the reasons with reliable data from global institutions and compares India with the top 3 global economies: USA, China, and Japan.
📊 India’s Economic Rise: The Numbers
- Rank: 4th (Overtook Germany)
- GDP: ~$4.1 Trillion (2024, Nominal)
- Source: IMF, World Bank
🚨 Challenges India Still Faces
1. 🧍♂️ Wealth Inequality
- Top 1% hold 40.1% of wealth
Source: World Inequality Report
2. 💼 Jobless Growth
- Unemployment rate ~8% (Youth: ~23%)
Source: CMIE, ILO
3. 👷♀️ Informal Sector Dominance
- ~90% in unorganised sector
Source: Ministry of Labour
4. 🏥 Low Public Spending
- Health: ~2.9% of GDP
- Education: ~3% of GDP
Source: World Bank
5. 🥣 Hunger Crisis
- Global Hunger Index Rank: 111/125
Source: GHI 2023
🌐 Global Comparison (Top 4 Economies)
| Metric | 🇺🇸 USA | 🇨🇳 China | 🇯🇵 Japan | 🇮🇳 India |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDP (Trillion $) | 28.8 | 18.8 | 4.4 | 4.1 |
| Poverty Rate | 11.5% | 0.6% | 15.7% | 21.9% |
| Hunger Rank (GHI) | – | Low | – | 111/125 |
| Unemployment | 3.9% | 5.2% | 2.6% | 7.8% |
| Per Capita Income | $86,000 | $13,500 | $35,000 | $2,700 |
📈 Conclusion
India’s growth story is remarkable, but inclusive development is key. To truly become a global leader, India must invest in:
- Job creation
- Public healthcare & education
- Formalizing the workforce
- Reducing wealth inequality